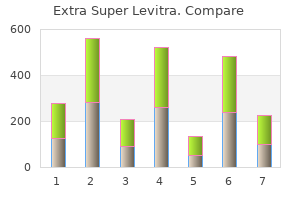
"Generic 100mg extra super levitra fast delivery, erectile dysfunction young age causes".
By: L. Grim, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Co-Director, University of Virginia School of Medicine
For example protocol for erectile dysfunction purchase extra super levitra 100mg with amex, if a shopper has already told you that they experience discomfort on a particular movement-rotation of their head to the best latest erectile dysfunction medications order extra super levitra 100 mg without a prescription, for example-it is sometimes a good idea to ask them to perform this explicit motion final erectile dysfunction doctors long island discount extra super levitra online visa. Clients with neck pain or a stiff neck have a tendency to twist at the waist and transfer their thorax so as to rotate to the right or to the left, instead of rotating their neck. Similarly, when asked to carry out lateral flexion, they typically tend to elevate their shoulders: if lateral flexion to the best is uncomfortable or tough, they raise their left shoulder, thus appearing to have the flexibility to move on this direction when in fact the movement is generated from their torso. If you see motion in the shoulders, instruct your client to begin once more, while preserving their shoulders stationary. Also, there may be a small group of individuals for whom caution is required when asking them to perform active actions involving the pinnacle and the neck. Another instance is if they report experiencing dizziness once they look as much as the ceiling. Question: When warning is required, what instructions might you give the client prior to them performing the test Instruct them to transfer their head slowly or to stop in the occasion that they feel in any method dizzy or unwell. One such guide is the Clinical Measurement of Joint Motion by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (Green and Heckman 1994). Norm = about 45 degrees 90� 0� 90� 0� 45� 0� Neutral position Example this individual has about forty five degrees of flexion. In this example, our subject has about 22 degrees of left lateral flexion, less than the norm. The illustrations at the prime of the desk are a reminder of the six movements you want to examine. For example, when you have not accomplished so already, you may discover that, as we age, the range through which we are able to actively transfer our neck decreases. Also, movement decreases in a number of ranges following harm if the shopper has not been properly rehabilitated; and people who regularly carry out yoga might have a rise in cervical range, or may keep their cervical vary for longer as they age. Subject Flexion Extension Right rotation Left rotation Right lateral flexion Left lateral flexion Mrs. That is, flexion, extension, lateral flexion (both left and right), and rotation (both left and right) all seem fine, with little or minimal discomfort. If you were to hold your neck flexed however look over your proper shoulder, you are now combining forward flexion with right rotation. Similarly, if you lookup into the sky and trace the trail of an plane because it passes overhead, your neck is in extension and will involve a degree of rotation, depending on which way the aircraft is moving. Begin with your consumer seated, ideally with their again supported and ft flat on the ground. Then, position your goniometer as proven in this tip and measure the totally different ranges. Follow the instructions supplied on the next pages to help you to measure flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation. Ask your client to take their chin as near their chest as potential and, as they do this, move the arm of the goniometer to keep it aligned with nares. Ask your shopper to take their head way again to attainable, trying to get the again of their head to contact the highest of their again. Position the middle of your goniometer over C7, with the stationary arm over the spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae and the moveable arm over the occipital protuberance. Instruct your shopper to maintain their shoulders still and down as they move their head to try to get their ear to contact the shoulder on that side. Keep the shifting arm in alignment with the occipital protuberance and take your measurement on the finish of range.
It enters the mandibular foramen to course within the alveolar canal and ends because the mental artery erectile dysfunction blood pressure medication purchase extra super levitra 100 mg online, which gives off an incisive branch earlier than exiting by way of the mental foramen to provide the chin erectile dysfunction caused by lipitor buy extra super levitra 100 mg fast delivery. The arterial supply of the tongue is erectile dysfunction ed treatment order online extra super levitra, for essentially the most half, by means of the lingual artery. The anastomoses between the branches of the right and left lingual arteries are of a small enough caliber in order that ligation of 1 artery makes that side of the tongue sufficiently cold for an operative process. Under cowl of the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle, the lingual artery provides off dorsal lingual branches, which journey superiorly and medial to the styloglossus muscle to provide the mucous membrane of the dorsum way again to the epiglottis, anastomosing with different vessels supplying the tonsil. The portion of the artery from the anterior border of the hyoglossus forward to the tip of the tongue is the deep lingual artery, which lies deep to the genioglossus muscle and is beneath cover of the mucous membrane on the inferior floor of the tongue. The mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth and the sublingual gland receive blood through the sublingual artery, which branches from the lingual near the anterior border of the hyoglossus muscle and courses anterior and superior to the mylohyoid muscle and lateral to the genioglossus. The muscular tissues of the floor of the mouth are equipped by the submental branch of the facial artery and the mylohyoid branch coming off from the inferior alveolar just earlier than it enters the mandibular foramen. These two arteries contribute some blood to the submandibular gland, which will get most of its provide from the nearby facial artery. The arterial provide of the palate is chiefly from the descending palatine branch of the third a part of the maxillary artery, which travels interiorly via the pterygopalatine canal to emerge from the greater palatine foramen and then programs anterior, medial to the alveolar course of, to anastomose at the incisive foramen with a septal branch of the sphenopalatine artery. The lesser palatine artery, which runs posteriorly from the descending palatine at the larger palatine foramen, provides the soft palate and anastomoses with other arteries that offer the tonsil. Anastomoses exist also with a palatine department of the ascending pharyngeal artery, the dorsal lingual arteries, and the ascending palatine from the facial artery. The pharynx receives blood from many sources, the amount from every source varying a fantastic deal individually. One of the chief sources is the ascending pharyngeal artery, usually from the external carotid artery. Other arteries that run to the pharynx and may thus contribute to its supply are the ascending palatine and tonsillar branches of the facial artery, the superior thyroid artery and its superior laryngeal department, and the inferior laryngeal and ascending cervical branches of the thyrocervical trunk from the subclavian artery. The pharyngeal branch of the third a part of the facial artery passes through a bony canal to reach the roof of the pharynx, and the descending palatine artery, additionally from the third part of the facial, contributes to the supply within the area of the tonsil by its lesser palatine branches. The veins in this area are inclined to lie more superficially than the arteries and type plexuses substituting for single, particular vessels. The inner jugular vein finally receives nearly the entire blood derived from the mouth and pharynx. This vein begins as a continuation of the sigmoid sinus on the jugular foramen and descends within the neck lateral to the interior and then common carotid arteries to about the stage of the sternoclavicular joint, the place it joins the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein. For essentially the most part, the arteries described within the previ- Submental vein ous section have veins of the same name accompanying Facial vein and artery them, but the veins into which these drain differ in varied ways from the branches of the external carotid Maxillary veins artery. Fre- External palatine vein quently, one encounters a middle thyroid vein with no Vena comitans of corresponding artery that also empties into the interior hypoglossal nerve jugular vein. Dorsal lingual vein coursing the deep lingual vein, often more than one channel, medial to hyoglossus muscle accompanies the corresponding artery from the tip of Lingual vein the tongue to the anterior border of the hyoglossus muscle, where the most important vein receives the sublingual Communication to vein after which accompanies the hypoglossal nerve on the anterior jugular vein (cut) lateral floor of the hyoglossus muscle, in addition to a Superior laryngeal vein smaller vein(s) that runs alongside the lingual artery. Superior thyroid vein Near the posterior border of the hyoglossus muscle, considered one of these veins receives the dorsal lingual veins, and Thyroid gland then they either join to type a short lingual vein or Middle thyroid vein proceed separately to empty either into the widespread Inferior thyroid veins facial vein or directly into the inner jugular vein. Termination of anterior the facial vein follows a not-so-tortuous path (com- jugular vein (cut) pared with the artery) from the medial angle of the eye to the lower border of the mandible near the anterior Left brachiocephalic vein margin of the masseter muscle. From here it programs posteriorly within the submandibular triangle (not as sheltered by the mandible because the artery) to join the anterior division of the retromandibular vein within the formation of a typical trunk that empties into the interior jugular vein.
This often describes the kind of posture where an individual has "rounded" shoulders impotence male purchase extra super levitra 100 mg without a prescription, their head craned too far ahead impotence medications buy 100 mg extra super levitra visa, not balanced over their thorax does erectile dysfunction cause low libido buy extra super levitra us. Clients with such postures have lengthened rhomboid muscles as a outcome of protraction of the scapulae, and shortened pectorals. Holding a chest stretched for around 30 seconds every day is more doubtless to lead to improved posture. Ten stretches illustrated on the next pages vary from the easy (stretches 1, 2, 3, and 4) to the more superior (5, 6, 7, and 8) and particular (9 and 10) stretches. Experiment with these examples, deciding on those you suppose are appropriate in your clients. Stretch 1 As rhomboid muscles are the antagonists to the pectorals, simply contracting rhomboids helps scale back tone in pectorals. Stretch 2 A trick is to ask a consumer merely to contact the again of their head as shown alongside. The pectorals are stretched if, as soon as in this position, your subject takes their elbows backward. Notice how various the position of the towel varies the location in the chest muscle the place the stretch is experienced. Extending the arms on this way with a towel is contraindicated for clients with a historical past of shoulder subluxations or dislocations. When a consumer has area and time obtainable, the following two chest stretches might be used. Stretch 5 the consumer rests within the supine position with a towel rolled up and placed lengthwise down the thorax. The head also needs assist, either with this towel or with a pillow; otherwise, it falls back, extending the neck and this can be uncomfortable. The advantage of utilizing a towel is that it can be folded or rolled to swimsuit the dimensions of the shopper. The drawback is that heavier clients may need something stronger in opposition to which to relaxation. Alternatively, they could squat, thus changing the position of their arms in that means. Stretch 7 Where a consumer has the edge of a wall available, they could stand close to the wall and experiment with stretching different fibers of their pectoralis main muscle tissue by altering the position of their arms. Stretches 9 and 10 There are various ways of stretching the pectoral muscular tissues, and it can be enjoyable to give a consumer the problem of experimenting and discovering for themselves the positions they find best. They are notably useful for purchasers who maintain static postures for lengthy durations of time as part of their work or hobbies and can be utilized each to relieve the ache of muscle pressure once it occurs and, prophylactically, on an everyday basis throughout the day for 30 seconds so as to decrease the chance of rigidity growing. A choice of upper again stretches has been supplied here and, as for chest stretches, these range from the straightforward (stretches 1, 2, three, and 4) to the more superior (5, 6, 7, and 8) stretches. Stretch 1 In the hug position, the scapulae protract and the rhomboids are lengthened. To improve the stretch, instruct your consumer to undertake this place and then to take their chin to their chest. Stretch 2 Rounding the back whereas standing or sitting, pushing the back upward, additionally stretches the rhomboid muscular tissues. Stretch 3 An different, which also stretches the thoracic erector spinae, is to around the again with head and neck flexion. As with stretch 2, the shopper must give consideration to contracting their abdominals in order to arch their back.
Trusted 100mg extra super levitra. Photograph - Ed Sheeran (Lyrics).
Stand behind them and draw your fingertips throughout the muscular tissues as if the client had been supine diabetes obesity and erectile dysfunction discount extra super levitra 100mg on-line. Some therapists ask the consumer to move their own arm erectile dysfunction medicine name in india purchase extra super levitra uk, however this engages the pectoral muscle and you might not wish to erectile dysfunction treatment bayer discount extra super levitra 100 mg visa do that. Another space where you would practice with set off spots is within the latissimus dorsi. With your client prone, gently palpate the muscle and when you find a young spot, merely grip the muscle between your fingers. Alternatively, grip or compress the tender spot and ask your consumer to abduct their arm, thus stretching the muscle. Many claims are actually being made with regard to the function and effectiveness of taping. Some types of taping are designed to prevent motion of tissues (or joints), whereas others are utilized with the intention of allowing-or even sometimes facilitating-movement. One example of when a tape could be applied to the thorax to prevent movement is the place a client has a single painful section of the backbone due to muscle spasming. Another instance of if you would possibly want to apply restrictive tape is when somebody has a painful intercostal, perhaps following a tear. As with the backbone, your purpose would be to limit movement in a few of the delicate tissues. Tape is finest utilized with the arm adducted-to forestall tensioning the intercostal muscles-but in apply this is difficult as a end result of so as to access the area your consumer needs to abduct their arm. With your shopper in a relaxed however "good" upright posture, there are lots of ways to apply tape. A widespread and simple method is solely to create a big cross form on the thorax, starting on the acromion and drawing your tape posteriorly to connect to the lower ribs on the opposite facet of the body. Flexible tape may be applied in a myriad of how but should always be applied not within the neutral position but with the spine flexed and shoulders protracted. With flexible tape the "wrinkles" that appear when a consumer stands upright are a desired impact, and producers declare this is conducive to the therapeutic process. On one other day, see how it feels to put on tape in the identical location, however of shorter size. Comments 278 Chapter 5 Thoracic Treatment You can experiment on this method with all tape shapes. Tape form Comments 280 Chapter 5 Thoracic Treatment Tip 22: Rocking In Tip 18 you discovered about rebounding as a attainable remedy for rib dysfunction. Some therapists incorporate it firstly of their therapy session to chill out muscular tissues; others resolve to leave it out as they vary their routines and add different abilities. Using your palms, gently push your shopper away from you and then roll them towards you. Like rebounding, this is a rhythmic movement, however unlike rebounding, which may be vigorous, rocking is gentle. Notice how, when you place your arms as described, your client is rocked away from you and back once more rather like the trunk of Question: How quick should I rock my consumer The effect of this is to deliver a few mild torsion within the spine, which could help with relaxing and "releasing" paraspinal muscular tissues. This chapter has offered you with a selection of techniques, some of which can already be familiar to you, whereas others may be new, that are listed under. For further selection, you may also like to try the following further methods.
The femoral department runs lateral to the exterior iliac and femoral arteries erectile dysfunction rates age generic 100mg extra super levitra, passes posterior to the inguinal ligament do erectile dysfunction pumps work buy generic extra super levitra 100 mg on-line, and erectile dysfunction doctor montreal purchase extra super levitra pills in toronto, after piercing the anterior layer of the femoral sheath and the fascia lata, ramifies within the superficial tissues and skin over the femoral triangle. The genitofemoral nerve and its branches carry lots of the efferent and afferent fibers to and from the widespread iliac, exterior iliac, and femoral arteries. The anterior rami of the sacral and coccygeal nerves, which, in distinction to the lumbar nerves, diminish in dimension as they progress inferiorly, divide and reunite to contribute to the sacral and coccygeal plexuses. These lie on the posterior wall of the pelvis, posterior to the ureters, inside iliac vessels, and intestinal coils, and anterior to the piriformis and coccygeus muscles. The inferior and smaller a half of the fourth lumbar nerve unites with the anterior ramus of the fifth lumbar nerve because the lumbosacral trunk, which, together with the anterior rami of the primary three and the higher part of the fourth sacral nerves, constitutes the sacral plexus. The decrease a part of the fourth sacral joins the fifth sacral and coccygeal nerves to type the small coccygeal plexus. Each nerve entering into the composition of these two plexuses receives postganglionic sympathetic fibers by means of a number of gray rami communicantes from an adjoining ganglion of the sympathetic trunk. Pregan- L4 L5 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 Co Coccygeal plexus Sacral plexus Pelvic splanchnic nerves (parasympathetics) Perforating cutaneous nerve (S2, 3) Nerve to levator ani and coccygeus (S3, 4) Perineal department of 4th sacral nerve Anococcygeal nerves Obturator nerve Inferior anal (rectal) nerve Dorsal nerve of penis/clitoris Perineal nerve and Posterior scrotal/labial branches Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve glionic parasympathetic fibers originate in the second to fourth sacral ranges of the spinal wire; they emerge with the second, third, and fourth sacral nerves and go away thereafter as pelvic splanchnic nerves. The sacral plexus, by convergence and fusion of its roots, develops right into a flattened band, from which many branches arise, earlier than the massive sciatic nerve passes via the higher sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. This massive nerve consists of a tibial part and a standard fibular part, which normally stay fused till about the decrease third of the thigh, however which can sometimes be separated at their points of origin or could divide earlier than the nerve leaves the pelvis. The nerve of the sacral plexus splits into anterior and posterior divisions, which, in some individuals, unite again to produce the nerves. The nerves to the piriformis, levator ani, and coccygeus muscular tissues pierce the anterior or pelvic surfaces of these muscles. The nerve to the obturator internus muscle (not to be confused with the obturator nerve) leaves the pelvis through the larger sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle, crosses the ischial backbone lateral to the pudendal nerve and inside pudendal vessels, reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen, and sinks into the pelvic surface of the obturator internus muscle. The pudendal nerve passes between the piriformis and coccygeus muscles, leaves the pelvis by way of the greater sciatic foramen, alongside the sciatic nerve, crosses posteroinferior to the ischial backbone (medial to the interior pudendal artery), and accompanies that vessel through the lesser sciatic foramen into the pudendal canal on the obturator internus fascia. As the nerve enters the canal, it offers off the inferior rectal nerve and shortly thereafter terminates by splitting into the perineal nerve and the dorsal nerve of the penis or clitoris, respectively. The inferior rectal nerve perforates the medial wall of the pudendal canal, crosses the ischioanal fossa obliquely with the inferior rectal vessels, and divides into branches that are the primary provide of the external anal sphincter, the lining of the decrease part of the anal canal, and the skin across the anus. Its branches communicate with the perineal branches of the posterior femoral cutaneous, fourth sacral, and perforating cutaneous nerves and the perineal nerve, which is the bigger terminal department of the pudendal nerve. This latter nerve runs anteriorly in the pudendal canal inferior to the internal pudendal artery, projecting toward the posterior border of the urogenital diaphragm, near which it divides into superficial and deep branches. The superficial one divides into medial and lateral posterior scrotal (or labial) nerves, which spread over the skin of the scrotum or labia majora, communicating with the perineal department of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. The deep branches supply the anterior elements of the exterior anal sphincter, the superficial and deep transverse perineal, bulbospongiosus, and ischiocavernosus muscles, in addition to the sphincter urethrae (and, in a subsidiary style, the levator ani). The dorsal nerve of the penis accompanies the inner pudendal artery in its course via the deep transversal perineal muscle and passes anterior to the pubic arch beneath cover of the ischiocavernosus muscle and corpus cavernosum penis. Passing through a niche between the inferior fascia and the apex of the urogenital diaphragm, the nerve involves lie alongside the dorsal artery of the penis and continues as far as the glans and the prepuce. In the female the dorsal nerve of the clitoris is smaller, but its distribution is similar. The distribution is comparable in the female, to the perineum, labia majora, and root of the clitoris. Its terminal twigs talk with the inferior rectal and perineal branches of the pudendal and terminal filaments of the ilioinguinal nerves.